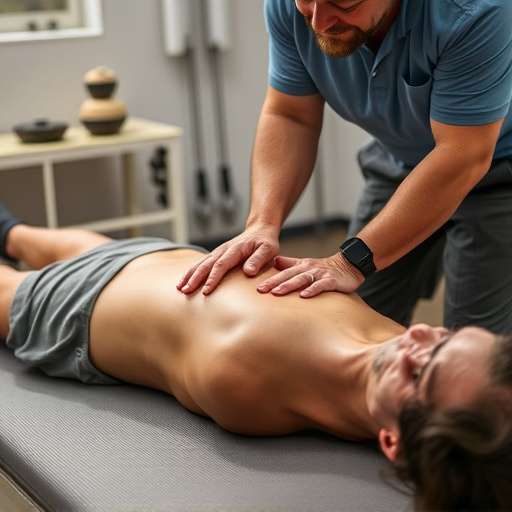
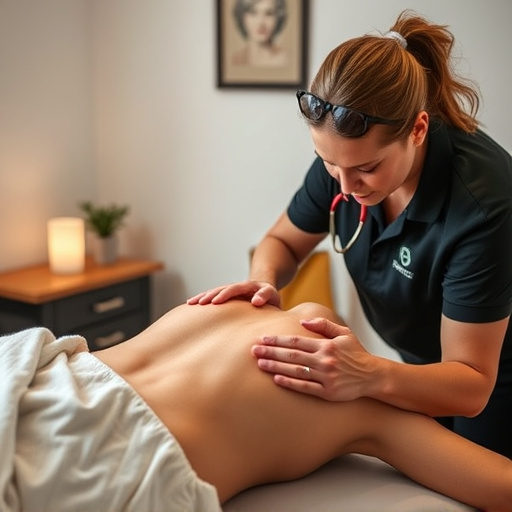
Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy (STST) is a non-invasive treatment using low-energy acoustic waves to accelerate healing of muscles, tendons, and ligaments, making it effective for auto accident recovery and chronic pain management. Ultrasound, traditionally a diagnostic tool, also offers therapeutic benefits in managing musculoskeletal issues and chronic pain with precise energy application. Both STST and ultrasound are complementary therapies chosen based on patient needs and conditions, ensuring optimal treatment for sports injuries or pinched nerve relief.
Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy (STST) has emerged as a powerful tool in the medical field, offering non-invasive treatment options for various soft tissue injuries. In this article, we delve into the world of STST and its comparison with ultrasound. Understanding these therapies’ distinct mechanisms is crucial when considering effective pain management and tissue regeneration. We explore how STST uses acoustic waves to promote healing, contrasting it with ultrasound’s use in diagnostic imaging and targeted therapy.
- Understanding Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy
- Exploring the Role of Ultrasound in Treatment
- Comparing Efficacy and Patient Experience
Understanding Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy
Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy (STST) is a non-invasive treatment that utilizes low-energy acoustic waves to promote healing and repair in soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments. This cutting-edge therapy has gained popularity in the fields of chiropractic care and functional rehabilitation due to its ability to stimulate cellular activity and accelerate tissue regeneration. STST works by transmitting high-intensity sound waves into the affected area, creating micro-traumata at a cellular level, which triggers a healing response from the body’s natural defense mechanisms.
Unlike traditional ultrasound, which uses high-frequency sound waves for diagnostic imaging, STST employs lower frequency shockwaves to penetrate deep into tissues. This targeted approach makes it highly effective in treating various conditions related to auto accident recovery and chronic pain management, offering a safe and non-painful alternative to surgical interventions or lengthy rehabilitation programs.
Exploring the Role of Ultrasound in Treatment
Ultrasound has long been a go-to tool in the medical field for various treatments, including managing musculoskeletal injuries and providing chronic pain relief. This non-invasive technique uses sound waves to penetrate deep into soft tissues, promoting healing and reducing inflammation. In the context of personal injury chiropractic care, ultrasound can be an effective adjunct therapy. It aids in accelerating the healing process by increasing blood flow to the affected area, which is crucial for delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to damaged muscles and tendons.
When compared to soft tissue shockwave therapy, ultrasound offers a more gentle approach. While both methods aim to alleviate pain and restore function, ultrasound typically targets specific areas with precise energy delivery. It’s particularly beneficial for patients who may not tolerate the higher pressure levels associated with shockwave therapy.
Comparing Efficacy and Patient Experience
When comparing Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy (STST) and Ultrasound for various conditions like sports injuries or back pain relief, understanding their efficacy and patient experience is crucial. STST has gained popularity for its ability to promote healing by stimulating soft tissues, making it an effective treatment for conditions such as tendinopathy, muscle strains, and pinched nerves. This non-invasive therapy uses high-energy sound waves to encourage the body’s natural healing process. On the other hand, ultrasound is a well-established technology used for diagnostic imaging, but it also has therapeutic applications. For certain conditions, ultrasound may provide similar benefits as STST in terms of reducing pain and inflammation, especially when targeting specific areas of the back or joints.
Patient experience varies between these two methods. STST is generally well-tolerated with minimal discomfort, often described as a gentle tapping sensation. The procedure is quick, usually taking around 15-30 minutes per session. In contrast, ultrasound therapy might be slightly more uncomfortable for some patients due to the continuous sound waves and potential heat generation, but modern techniques have significantly improved patient comfort. Both therapies offer advantages and are often used as complementary treatments, with healthcare professionals choosing based on individual patient needs and the specific condition being addressed, whether it’s for sports injury treatment or achieving pinched nerve relief.
Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy and ultrasound each offer unique advantages in treating soft tissue injuries. Shockwave therapy proves effective for chronic conditions resistant to conventional treatments, while ultrasound excels in reducing pain and inflammation acutely. The choice between them depends on the specific condition, patient tolerance, and treatment goals. For optimal outcomes, consulting a qualified healthcare professional is essential to determine the most suitable approach.