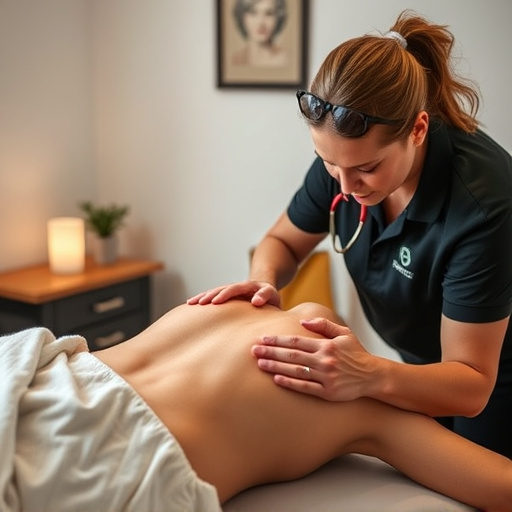
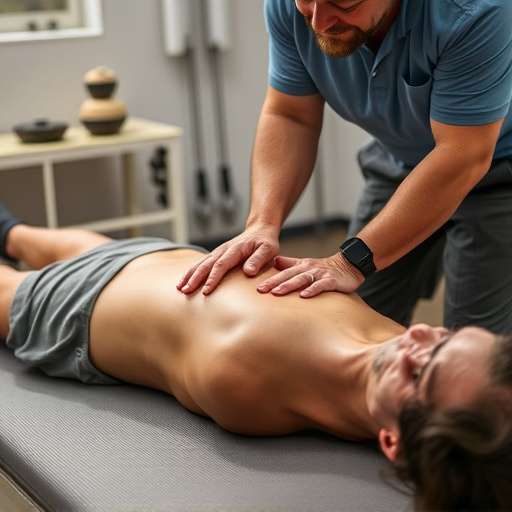
Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy (STST) is a non-invasive, effective treatment for tendon and ligament injuries using low-energy sound waves to stimulate healing. By promoting angiogenesis and fibroblast activation, STST reduces recovery times and pain compared to traditional methods, with minimal risks or downtime. This innovative therapy is well-tolerated, but success depends on factors like injury severity and patient health. Ongoing research suggests its potential in managing various soft tissue pathologies, making it an appealing option for comprehensive pain management in sports medicine.
“Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy: Revolutionizing Tendon and Ligament Care
In the realm of sports medicine, Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy (STST) emerges as a game-changer for treating tendon and ligament injuries. This non-invasive approach leverages concentrated acoustic waves to stimulate healing, offering a promising alternative to surgical interventions. STST promotes tissue regeneration, reduces pain, and enhances mobility. Understanding its mechanism and exploring its benefits, considerations, and future prospects can shed light on its potential as a premier treatment option in today’s digital era.”
- Understanding Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy: A Non-Invasive Approach
- How Does it Work for Tendons and Ligaments?
- Benefits, Considerations, and Future Prospects
Understanding Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy: A Non-Invasive Approach

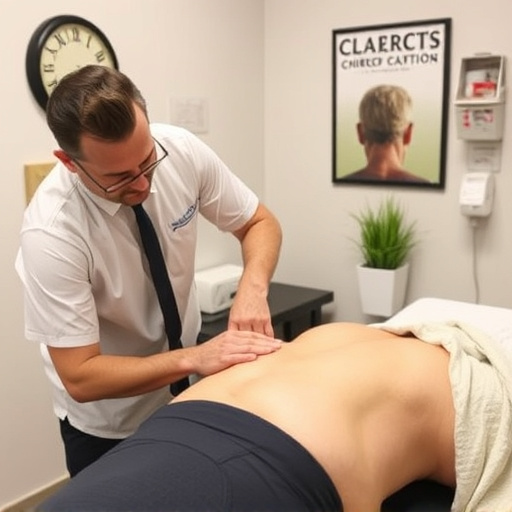
Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy (STST) represents a non-invasive approach to treating tendon and ligament injuries, offering a promising alternative to traditional surgical interventions. This innovative technique leverages low-energy sound waves, known as shockwaves, to stimulate healing and promote tissue regeneration directly within the affected areas. STST is particularly effective for post-injury care, aiming to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and enhance the body’s natural healing mechanisms without the need for incisions or anaesthesia.
By navigating the intricate landscape of soft tissues, shockwaves initiate a series of biological responses that include angiogenesis (the growth of new blood vessels) and fibroblast activation, both crucial elements in injury rehabilitation. This non-invasive method has gained traction in the field of sports medicine due to its ability to expedite recovery times and improve patient outcomes, making it an appealing option for managing tendon and ligament injuries as part of a comprehensive pain management strategy.
How Does it Work for Tendons and Ligaments?
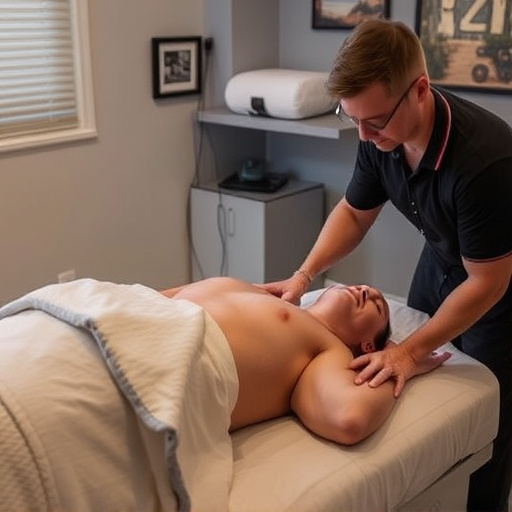
Soft tissue shockwave therapy works by using acoustic waves to stimulate a healing response in damaged tendons and ligaments. These high-energy sound waves penetrate deep into the soft tissues, creating micro-traumas that initiate a natural healing process. This non-invasive treatment is often used as an alternative to surgical interventions or as part of comprehensive rehab services.
By promoting blood flow and stimulating the release of growth factors, shockwave therapy accelerates the body’s natural repair mechanisms. This can result in reduced pain, improved tendon and ligament strength, and faster recovery times compared to traditional chiropractic treatment methods. The non-invasive nature of this approach makes it an attractive option for those seeking effective healing without the risks or downtime associated with more invasive procedures.
Benefits, Considerations, and Future Prospects
Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy (STSWT) has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of treating tendon and ligament injuries, offering numerous benefits for athletes and active individuals suffering from chronic soft tissue pain. One of its key advantages is accelerated muscle recovery, which can significantly reduce downtime and improve overall mobility. This non-invasive therapy stimulates the body’s natural healing process by delivering low-energy acoustic waves to injured areas, promoting tissue regeneration and breaking down scar tissue that often impedes movement.
When considering STSWT for soft tissue injuries, it’s essential to weigh its effectiveness against potential side effects and patient suitability. While generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience temporary discomfort or mild bruising at the treatment site. The success of this therapy also depends on factors such as the severity of the injury, the patient’s age, and their overall health. Looking ahead, ongoing research suggests that STSWT could be a promising approach for various soft tissue pathologies, potentially opening doors to personalized treatment plans and improved pain management strategies in the future.
Soft Tissue Shockwave Therapy (STST) emerges as a promising non-invasive treatment for tendon and ligament injuries, offering significant benefits such as reduced pain, improved function, and accelerated healing. As research continues to evolve, STST’s role in sports medicine and rehabilitation is expected to grow, potentially transforming the way we address soft tissue pathologies. However, considering potential side effects and contraindications is essential for optimal patient outcomes. Embracing this innovative approach could pave the way for more effective and efficient treatment strategies in the future.